Using Terminal
- Creating a Java program
- Compiling a Java program
- Executing a Java program
- Understanding a Java program
- Creating your own Java program
Errors
- Compile-time errors
- Run-time errors
- Logical errors

Classwork:
Standard Drawing

Suppose that the standard input stream is a sequence of double values. Write a program that takes an integer N and two double values left and right from the command line, StdIn, or Scanner and uses StdDraw to plot a histogram of the frequency of the numbers in the standard input stream that fall in each of the N intervals defined by dividing (left , right) into N equal-sized intervals.
The intervals’ marks and labels are optional.
Assumption: data values range from 0 to 100
Extra challenge: no range of values is known.
For development purpose ONLY, you can hard code the data or have a text file with the data. Make sure you have at least 30 data values with a good amount of variation in the values. Take a screenshot and turn in both the image and the data values.
Suggestion:
– Start by drawing a rectangle given the width and height as input.
– Next, draw n number of rectangles given the width, both n and width as input. For learning purposes, use a sample array of integers representing the frequency (the height of each rectangle) at each position.
– Last, replace the array of integers with the frequency of integers from the input stream based on the above specification. At this point you can add to your implementation the other constraints, left, right and N.
Homework:
Complete missing assignments.
Create a new folder in your Java folder, Unit_2.

Create a new project in Unit_2, InputOutput or InOut


Add the available StdLib classes to your project via the Edit tab, drag them or create them in your project.

Your project you look like this:

Let’s test our project with this program:
NOTE: include documentation and attach the image (screenshot)
/**
* Write a description of class Triangle here.
*
* @author (your name)
* @version (a version number or a date)
*/
public class Triangle
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
StdDraw.line(0,0,.1,.1);
StdDraw.line(0,0,0,1);
StdDraw.line(0,0,1,0);
}
}
Write a java program, MyRandArt_YI.java to create an abstract painting using the geometric functions in the StdDraw library and the random function to generate points, colors, and thickness. Note: make sure to restrict ranges for each feature.
Geometric Abstract Painting: Mary Heilmann

Students’ work from previous years
How to create your own colors:
setPenColor(int red, int green, int blue)
Creates an opaque RGB color with the specified red, green, and blue values.
Parameters:
red – the amount of red (between 0 and 255)
green – the amount of green (between 0 and 255)
blue – the amount of blue (between 0 and 255)
How to draw a polygon:

Write a short program with a polygon and play with it until you understand how it works.
[spoiler title=’APoly’]
/**
* Playing with colors and shapes.
*
* @GE
* @java 1.8.4
* 12/5/18
*/
public class APoly
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
// rescale the coordinate system
StdDraw.setXscale(0, 2);
StdDraw.setYscale(0, 2);
StdDraw.setPenColor(255,0,255);
double y[] = {.5,.5,1.5,1.5}; // y coordinates of each vertex
double x[] = {.5,1.5,1.5,.5}; // x coordinates of each vertex
//StdDraw.setPenColor(255,0,255);
StdDraw.filledPolygon(x,y);
StdDraw.setPenColor(0,0,255);
StdDraw.setPenRadius(0.008);
StdDraw.polygon(x,y);
}
}
[/spoiler]

How to change thickness:
setPenRadius(0.05)
Sets the pen size to the default size (0.002). The pen is circular, so that lines have rounded ends, and when you set the pen radius and draw a point, you get a circle of the specified radius.
Write a program Circles_YI.java that draws filled circles of random size at random positions in the unit square, producing images like those below. Your program should take four command-line arguments: the number of circles, the probability that each circle is black, the minimum radius, and the maximum radius.
Submit screenshots and submit them.
Classwork: PU Input and Output Standard classes
You can get the following files from edmodo.com. Add them to your workspace:
StdIn.java
StdOut.java
StdDraw.java
StdAudio.java
7. What is an abstraction for an infinite output sequence?
8. These are the same as System.out. Why not just use System.out?
9. Interactive input
• Prompt user to type inputs on standard input stream.
• Mix input stream with output stream.
10. Average
• Read a stream of numbers.
• Compute their average.
11. How do I specify the end of the stream?
12. What is the limit on the size of the input stream?
13. Do I always have to type in my input data and print my output?
14. What can you do if there’s no room for a huge file on my computer?
Formatted printing basics again. In its simplest form, printf() takes two arguments. The first argument, a string, contains a format that describes how the second argument is to be converted to a string for output.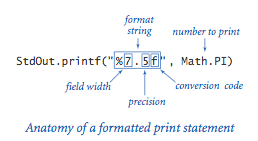

15. How many spaces are printed before the digit 3 in the following line: StdOut.printf(“%8.3f”, Math.PI);?
More on re-directing input/output
/******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac PlotFilter.java
* Execution: java PlotFilter < input.txt
* Dependencies: StdDraw.java StdIn.java
*
* % java PlotFilter < USA.txt
*
* Datafiles: http://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/java/15inout/USA.txt
*
******************************************************************************/
public class PlotFilter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// read in bounding box and rescale
double x0 = StdIn.readDouble();
double y0 = StdIn.readDouble();
double x1 = StdIn.readDouble();
double y1 = StdIn.readDouble();
StdDraw.setXscale(x0, x1);
StdDraw.setYscale(y0, y1);
// for bigger points
StdDraw.setPenRadius(0.005);
// to speed up performance, defer displaying points
StdDraw.enableDoubleBuffering();
// plot points, one at a time
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
double x = StdIn.readDouble();
double y = StdIn.readDouble();
StdDraw.point(x, y);
}
// display all of the points now
StdDraw.show();
}
}

Use the java programs from the lesson, Triangle.java, PlotFilter.java, and FunctionGraph.java to work on the assignments posted on edmodo.com.
MyPlotFilter_YI.java
Use PlotFilter.java from Filtering data to a standard drawing to create your own drawing.
Read about Standard drawing and the Methods Summary
Classwork:
Write a program, MyGraphPaper_YI.java similar to CheckerBoard.java from below but to draw 2 different kinds of graph paper. Think of what graph paper you would use in a math class.
Study program CheckerBoard.java that takes a command-line argument N and plots an N-by-N checkerboard with red and black squares. It colors the lower left square red.

[spoiler title=’Checkerboard.java’]
Below is the syntax highlighted version of Checkerboard.java from §1.5 Input and Output.
/******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac Checkerboard.java
* Execution: java Checkerboard n
* Dependencies: StdDraw.java
*
* Plots an n-by-n checkerboard.
*
******************************************************************************/
public class Checkerboard {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
StdDraw.setXscale(0, n);
StdDraw.setYscale(0, n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if ((i + j) % 2 != 0) StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.BLACK);
else StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.RED);
StdDraw.filledSquare(i + 0.5, j + 0.5, 0.5);
}
}
}
}
Copyright © 2000–2017, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
Last updated: Fri Oct 20 14:12:12 EDT 2017.
[/spoiler]
RandomBlock_YI.java Animation
Use the tools from the BouncingBall program to implement RandomBlock_YI.java. This program re-uses the program from the graph paper assignment and randomly select squares on the grid that will become a solid color or “alive” and then randomly it will become back to white or “dead” again.
public final class StdOut extends Object
StdOut.class in your Java classpath. If you used our autoinstaller, you should be all set. Otherwise, either download stdlib.jar and add to your Java classpath or download StdOut.java and put a copy in your working directory.
Here is an example program that uses StdOut:
public class TestStdOut {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 17;
int b = 23;
int sum = a + b;
StdOut.println("Hello, World");
StdOut.printf("%d + %d = %d\n", a, b, sum);
}
}
Differences with System.out. The behavior of StdOut is similar to that of System.out, but there are a few technical differences:
StdOut coerces the character-set encoding to UTF-8, which is a standard character encoding for Unicode.StdOut coerces the locale to Locale.US, for consistency with StdIn, Double.parseDouble(String), and floating-point literals.StdOut flushes standard output after each call to print() so that text will appear immediately in the terminal.Reference. For additional documentation, see Section 1.5 of Computer Science: An Interdisciplinary Approach by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
| Modifier and Type | Method and Description |
|---|---|
static void |
main(String[] args)
Unit tests some of the methods in
StdOut. |
static void |
print()
Flushes standard output.
|
static void |
print(boolean x)
Prints a boolean to standard output and flushes standard output.
|
static void |
print(byte x)
Prints a byte to standard output and flushes standard output.
|
static void |
print(char x)
Prints a character to standard output and flushes standard output.
|
static void |
print(double x)
Prints a double to standard output and flushes standard output.
|
static void |
print(float x)
Prints a float to standard output and flushes standard output.
|
static void |
print(int x)
Prints an integer to standard output and flushes standard output.
|
static void |
print(long x)
Prints a long integer to standard output and flushes standard output.
|
static void |
print(Object x)
Prints an object to standard output and flushes standard output.
|
static void |
print(short x)
Prints a short integer to standard output and flushes standard output.
|
static void |
printf(Locale locale, String format, Object... args)
Prints a formatted string to standard output, using the locale and the specified format string and arguments; then flushes standard output.
|
static void |
printf(String format, Object... args)
Prints a formatted string to standard output, using the specified format string and arguments, and then flushes standard output.
|
static void |
println()
Terminates the current line by printing the line-separator string.
|
static void |
println(boolean x)
Prints a boolean to standard output and then terminates the line.
|
static void |
println(byte x)
Prints a byte to standard output and then terminates the line.
|
static void |
println(char x)
Prints a character to standard output and then terminates the line.
|
static void |
println(double x)
Prints a double to standard output and then terminates the line.
|
static void |
println(float x)
Prints an integer to standard output and then terminates the line.
|
static void |
println(int x)
Prints an integer to standard output and then terminates the line.
|
static void |
println(long x)
Prints a long to standard output and then terminates the line.
|
static void |
println(Object x)
Prints an object to this output stream and then terminates the line.
|
static void |
println(short x)
Prints a short integer to standard output and then terminates the line.
|
public static void println()
public static void println(Object x)
x – the object to printpublic static void println(boolean x)
x – the boolean to printpublic static void println(char x)
x – the character to printpublic static void println(double x)
x – the double to printpublic static void println(float x)
x – the integer to printpublic static void println(int x)
x – the integer to printpublic static void println(long x)
x – the long to printpublic static void println(short x)
x – the short to printpublic static void println(byte x)
BinaryStdOut.
x – the byte to printpublic static void print()
public static void print(Object x)
x – the object to printpublic static void print(boolean x)
x – the boolean to printpublic static void print(char x)
x – the character to printpublic static void print(double x)
x – the double to printpublic static void print(float x)
x – the float to printpublic static void print(int x)
x – the integer to printpublic static void print(long x)
x – the long integer to printpublic static void print(short x)
x – the short integer to printpublic static void print(byte x)
x – the byte to print<pre>public static void printf(String format, Object... args)</pre>
format – the format stringargs – the arguments accompanying the format stringpublic static void printf(Locale locale, String format, Object... args)
locale – the localeformat – the format stringargs – the arguments accompanying the format stringpublic static void main(String[] args)
StdOut.args – the command-line arguments